o dermal tissue
o vascular tissue
o ground tissue
Dermal tissue
- covers and protects plants.
- Includes the epidermis and modified cells like guard cells, root hairs, and cells that produce a waxy cuticle.
Below are the dermal layers of a leaf
Vascular tissue
- consists of phloem and xylem
- these transport water and nutrients around the plant
xylem
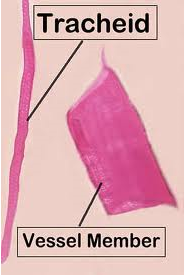
- the water and mineral conducting tissue, consists of two types of elongated cells: tracheids and vessel elements
- both tracheids and vessel elements are dead at functional maturity.
- Seedless vascular plants and most gymnosperms have only tracheids
- Angiosperms have both tracheids and vessel members
- Xylem is what makes up wood.
Wood
*Tracheids - long thin cells that overlap and are tapered at the ends.
* Vessel elements - generally wider, shorter, thinner walled and less tapered than tracheids.
- aligned end to end and differ from tracheids in that the ends are perforated to allow free flow through the vessel tubes.
Phloem
- carries sugars from the photosynthetic leaves to the rest of the plant by active transport.
- Consists of chains of sieve tube members or elements whose end walls contain sieve plates that facilitate the flow of fluid from one cell to the next.
- Alive at functional maturity, although they lack nuclei, ribosome and vacuoles. Connected to each sieve tube member is at least one companion cell that does contain a full complement of cell organelles and nurtures the sieve tube elements.
Below is an image of a sieve tube member
Ground tissue
- the most common type of tissue
- functions mainly as support, storage and photosynthesis
- consists of three cell types: parenchyma, sclerenchyma and collenchyma
Below are ground tissue cells
Parenchyma cells
- look like classic plant cells
- have primary cells walls that are thin and flexible
- lack secondary cell walls
- protoplasm contains one large vacuole and the cell carries out most metabolic functions
- parenchymal cells in the leaf (mesophyll cells) contain chloroplasts and carry out photoynthesis
- parenchymal cells in roots contain plastids and store starch
- if turgid with water, they give support and shape to the plant.
- Most parenchymal cells retain the ability to divide and differentiate into other cell types after a plant has been injured in some way.
- Once parenchymal cell may regenerate or clone an entire plant
Collenchyma cells
- have unevenly thickened primary cell walls but lack secondary cell walls
- mature collenchymal cells are alive and their function is to support the growing stem
Scelerenchyma cells
- have thick primary and secondary cell walls fortified with lignin
- function is to support the plant
- two forms: sclereids and fibers
* fibers – are long thin and fibrous like and usually occur in bundles
- commercially used to make rope and flax fibers
* sclereids – short and irregular in shape.
- make up tough seed coats and pits
- give pears its gritty texture






2 comments:
thank you sir... :))
We seek permission to use images for educational purposes at UNiversity of Delhi.
www.vle.du.ac.in
Post a Comment